Product risk is the possibility that the system or software might fail to satisfy or fulfill some reasonable expectation of the customer, user, or stakeholder. (Some authors also called the ‘Product risks’ as ‘Quality risks’ as they are risks to the quality of the product.) [Read more…] about What is Product risk in software testing?
Software
What is configuration management in software testing?
Configuration management is a topic that often confuses new practitioners. So, let me describe it briefly:
- Configuration management determines clearly about the items that make up the software or system. These items include source code, test scripts, third-party software, hardware, data and both development and test documentation.
- Configuration management is also about making sure that these items are managed carefully, thoroughly and attentively during the entire project and product life cycle.
- Configuration management has a number of important implications for testing. Like configuration management allows the testers to manage their testware and test results using the same configuration management mechanisms.
- Configuration management also supports the build process, which is important for delivery of a test release into the test environment. Simply sending Zip archives by e-mail will not be sufficient, because there are too many opportunities for such archives to become polluted with undesirable contents or to harbor left-over previous versions of items. Especially in later phases of testing, it is critical to have a solid, reliable way of delivering test items that work and are the proper version.
- Last but not least, configuration management allows us to keep the record of what is being tested to the underlying files and components that make it up. This is very important. Let us take an example, when we report defects, we need to report them against something, something which is version controlled. If it is not clear what we found the defect in, the programmers will have a very tough time of finding the defect in order to fix it. For the kind of test reports discussed earlier to have any meaning, we must be able to trace the test results back to what exactly we tested.
Ideally, when testers receive an organized, version-controlled test release from a change-managed source code repository, it is along with a test item trans-mittal report or release notes. [IEEE 829] provides a useful guideline for what goes into such a report. Release notes are not always so formal and do not always contain all the information shown.
Configuration management is a topic that is very complex. So, advanced planning is very important to make this work. During the project planning stage – and perhaps as part of your own test plan – make sure that configuration management procedures and tools are selected. As the project proceeds, the configuration process and mechanisms must be implemented, and the key interfaces to the rest of the development process should be documented.
What is test monitoring in software testing?
Test monitoring can serve various purposes during the project, including the following:
- Give the test team and the test manager feedback on how the testing work is going, allowing opportunities to guide and improve the testing and the project.
- Provide the project team with visibility about the test results.
- Measure the status of the testing, test coverage and test items against the exit criteria to determine whether the test work is done.
- Gather data for use in estimating future test efforts.
[Read more…] about What is test monitoring in software testing?
What are the estimation techniques in software testing?
There are two techniques for estimation covered by the ISTQB Foundation Syllabus.
- One involves people with expertise on the tasks to be done and
- Other involves consulting the people who will do the work .
The first one involves analyzing metrics from past projects and from industry data.
Let’s look at both of them one by one. [Read more…] about What are the estimation techniques in software testing?
What is Dynamic testing technique? Examples, Types, Advantages & Disadvantages
Dynamic testing technique is the type of testing that validates the functionality of an application when the code is executed / by executing the code. In simple terms dynamic testing is performed by actually using the application and seeing if a functionality works the way it is expected to. There is also something called ‘static’ testing. Learning about static testing helps understand dynamic testing better, so let’s summarize static testing first.
What is Static Testing?
Static testing as the name itself suggests is static in nature, which also means there are no changing conditions or parameters. In other words, this is performed without executing the code.
For example, when you are verifying a document or testing a document, you will go through the document, review it and then suggest or make changes.
Also, when there is a code review / walkthrough, the development team goes over the code step by step and checks whether the code written is according to the development standards and also it traverses through correctly to achieve the results desired.
Since, we are not changing anything in the documents, but also reviewing them, it is called static testing. We are testing, but it is static in nature.
Other examples for static testing are review of test strategy document, test plan document, test case walkthrough, Inspection of the code etc.
What is Dynamic Testing?
Now, let’s look at Dynamic testing. The name itself suggests that it is “Dynamic” in nature, which means changing. This is the kind of testing that we do with changing values or conditions by executing the code.
This involves testing the application in real-time by giving inputs and examining the result or the output value of behavior.
Dynamic Testing Example
The easiest example to understand this is the login functionality of any application, like Google’s gmail.com. If we are creating an account, and a password for the account, you would have certain rules for creating a strong password.
For instance, 8 characters long, needs to have a capital letter and at least one special character.
These are nothing but different conditions or parameters and if the user inputs any value that deviate from these rules, the application should either warn or reject.
If you are testing this functionality as an example, you would input all the conditions required to test this and then validate the output.
You would also input the non-working parameters, for example, input a 4-character password and verify if there is an error that is thrown. This is all part of Dynamic testing.
Types of Dynamic Testing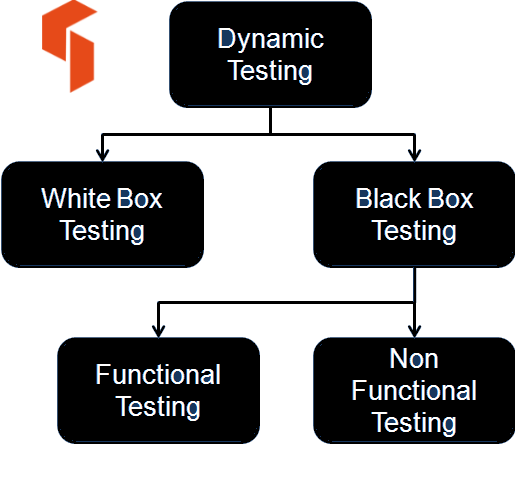
Dynamic testing is broadly classified into two types.
- Whitebox testing – Whitebox testing looks at the internal workings of the code. For this type of testing, the tester should know the code development, review and be able to interpret the code.
- Blackbox testing – Blackbox testing looks at only the functionality of the Application Under Test (AUT). This does not require the tester to know the implementation details or be able to interpret the inner workings of the code. This is the type of testing mostly done by the QA department.
Since we are interested more in learning about Blackbox testing, we also need to know that there are again two broad types of Blackbox testing.
- Functional Testing – As the name itself suggests, this is the type of testing that validates the functionality of the application.
- Non-Functional Testing – Non-Functional testing covers the aspects of performance, recovery, compatibility testing etc. These are non-functional in nature. And there may be a separate division in the organizations to do the non-functional testing.
Dynamic testing is performed at different levels. Let’s look at the basic definition of what each testing means.
- Unit testing – Simply put, the testing done by the developers right after they build the code to ensure their code is working as they expected and according to the requirements.
- System testing – This is the type of testing the QA department does after the code has been built and this covers the entire system/application in terms of testing. The QA team does thorough testing to make sure the functionality of the system is in-line with the requirements.
- Integration testing – This is a joint effort (in most companies) by the QA and development teams to make sure each individual module (after being tested) then connected to other modules or systems is still working as expected. This is basically the testing for the entire workflow from start to end.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT) – This is done by the UAT team (User Acceptance Testing) with the aid of QA team. The business users write their own test cases and perform testing more geared towards the user’s perspective unlike what the QA does, more toward system’s perspective.
There are advantages to using dynamic testing. At the same time there are some disadvantages. Let’s look at the advantages first.
Advantages of Dynamic Testing
- Dynamic testing is thorough, which looks at in-depth functionality of the application so the quality is of highest standards.
- Dynamic testing process is well-established and hence the application is tested from user’s and business perspective thus increasing the quality standards.
- Complex defects can be caught which may have escaped the review processes
- Dynamic testing can be automated using tools
Disadvantages of Dynamic Testing
- Since Dynamic testing follows a complex detailed process, it takes time.
- It is time consuming and it costs more money to the organizations because of the need for the resources and time.
- Dynamic testing is usually performed after coding is completed and hence defects are discovered later in the lifecycle
In a nutshell, Dynamic testing technique is the type that is followed in all the organizations today. It is used as a tool that the QA can rely on and has successfully shown results of higher quality when followed properly in organizations. This is extremely useful technique in software testing.
