An iterative life cycle model does not attempt to start with a full specification of requirements. Instead, development begins by specifying and implementing just part of the software, which can then be reviewed in order to identify further requirements. This process is then repeated, producing a new version of the software for each cycle of the model.
For example:

In the diagram above when we work iteratively we create rough product or product piece in one iteration, then review it and improve it in next iteration and so on until it’s finished. As shown in the image above, in the first iteration the whole painting is sketched roughly, then in the second iteration colors are filled and in the third iteration finishing is done. Hence, in iterative model the whole product is developed step by step.
Diagram of Iterative model:
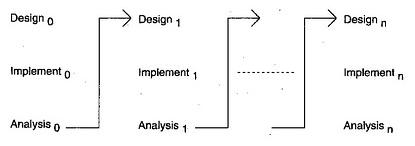
Advantages of Iterative model:
- In iterative model we can only create a high-level design of the application before we actually begin to build the product and define the design solution for the entire product. Later on we can design and built a skeleton version of that, and then evolved the design based on what had been built.
- In iterative model we are building and improving the product step by step. Hence we can track the defects at early stages. This avoids the downward flow of the defects.
- In iterative model we can get the reliable user feedback. When presenting sketches and blueprints of the product to users for their feedback, we are effectively asking them to imagine how the product will work.
- In iterative model less time is spent on documenting and more time is given for designing.
Disadvantages of Iterative model:
- Each phase of an iteration is rigid with no overlaps
- Costly system architecture or design issues may arise because not all requirements are gathered up front for the entire lifecycle
When to use iterative model:
- Requirements of the complete system are clearly defined and understood.
- When the project is big.
- Major requirements must be defined; however, some details can evolve with time.
Other models you should know about are:
Other popular articles:
- What is Incremental model- advantages, disadvantages and when to use it?
- What is V-model- advantages, disadvantages and when to use it?
- What is Prototype model- advantages, disadvantages and when to use it?
- What is RAD model- advantages, disadvantages and when to use it?
- What are the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) phases?
Gyau Samuel says
Please who is the Author of this blog
ISTQB Guide says
The author’s name is S Kumar.
Getnet shiferaw says
what are simple example of iterative model tell me some example?
zia says
When the customer don’t know in advance what are the actual and real requirements for the proposed system, and the particular requirements from customer side are ambiguous; then according to your opinion what type of process model should be used to get the actual requirements of proposed system?
Rupam says
Any one can berif the difference between incremental model and iterative model.
Shakeel says
The difference between Incremental and Iterative models
• In incremental model, it is clear at start what we want to develop but we develop it step by step by breaking it in different modules.
• In iterative model, you build on the top of the existing product and continuously improve it to end up with something new.
Vijay Verma says
I am an android developer and I want to make an app of your website as your webpage is more clear and have enough knowledge and it also helps me a lot.
So please contact me soon.
Thank you.
Fasil says
When to use iterative model:
Requirements of the complete system are clearly defined and understood
Is it correct